Health-saving technologies in the educational process
Currently, medical workers note a significant decrease in the number of absolutely healthy children, a rapid increase in the number of functional disorders and chronic diseases, a sharp increase in the proportion of pathologies of the nervous system, cardiovascular and digestive systems, and the musculoskeletal system.
There is a significant deterioration in the health of children associated with an increase in the volume and complexity of the educational workload, the complication of the nature of the “student-teacher” relationship, lack of physical activity, poor nutrition of students, non-compliance with hygienic requirements in the organization of the educational process, lack of basic knowledge among students about how to become healthy [3].
In this regard, one of the activities of a modern school is to preserve the health of schoolchildren. For this purpose, health-saving technologies are used, which involve a combination of pedagogical, psychological and medical influences aimed at protecting and ensuring health, and forming a valuable attitude towards it.
A healthy lifestyle does not yet occupy first place in the hierarchy of human needs and values in our society. But if we organize an educational environment based on health-saving technologies, teach children from a very early age to value, take care of and strengthen their health, if we demonstrate a healthy lifestyle by personal example, then only in this case can we hope that future generations will be healthier and developed not only personally, intellectually, spiritually, but also physically.
The health of a child, his socio-psychological adaptation, normal growth and development are largely determined by the environment in which he lives. For a child from 6 to 17 years old, this environment is the education system, since more than 70% of his waking time is associated with being in educational institutions. At the same time, during this period the most intensive growth and development occurs, the formation of health for the rest of life, the child’s body is most sensitive to exogenous environmental factors.
According to the Institute of Developmental Physiology of the Russian Academy of Education, the school educational environment creates risk factors for health problems, the action of which is associated with 20-40% of the negative influences that worsen the health of school-age children. Research by the Institute of VF RAO makes it possible to rank school risk factors in descending order of importance and strength of influence on the health of students:
- stressful pedagogical tactics;
- inconsistency of teaching methods and technologies with the age and functional capabilities of schoolchildren;
- failure to comply with basic physiological and hygienic requirements for organizing the educational process;
- insufficient literacy of parents in matters of maintaining children's health;
- failures in the existing system of physical education;
- intensification of the educational process;
- functional illiteracy of the teacher in matters of health protection and promotion;
- partial destruction of school medical control services;
- lack of systematic work to develop the value of health and a healthy lifestyle.
Thus, the traditional organization of the educational process creates constant stress overloads in schoolchildren, which lead to breakdown of the mechanisms of self-regulation of physiological functions and contribute to the development of chronic diseases. As a result, the existing school education system is health-costly.
Many teachers believe that administrators and specially trained professionals should be involved in preserving and strengthening the health of students at school. However, an analysis of school risk factors shows that the majority of students’ health problems are created and solved during the daily practical work of teachers, i.e., associated with their professional activities. Therefore, the teacher needs to find reserves for his own activities in preserving and strengthening the health of students.
The lesson remains the main organizational form of the educational process, which directly depends on the teacher. Identifying criteria for the health-saving potential of a school lesson and building a lesson on a health-saving basis is the most important condition for overcoming the health-intensive nature of school education.
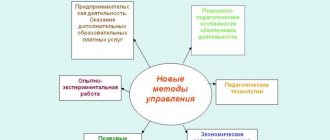
“Health-forming educational technologies”, as defined by N.K. Smirnov, are all those psychological and pedagogical technologies, programs, methods that are aimed at nurturing in students a culture of health, personal qualities that contribute to its preservation and strengthening, the formation of an idea of health as values, motivation to lead a healthy lifestyle.
Health-saving technology, according to V.D. Sonkin, is:
- conditions for a child’s education at school (lack of stress, adequacy of requirements, adequacy of teaching and upbringing methods);
- rational organization of the educational process (in accordance with age, gender, individual characteristics and hygiene requirements);
- compliance of educational and physical activity with the age capabilities of the child;
- necessary, sufficient and rationally organized motor mode.
Health-saving educational learning technologies include the following components:
- optimal level of difficulty, variability of teaching methods and forms;
- optimal combination of motor and static loads;
- small group training;
- use of clarity;
- a combination of different forms of information provision;
- creating an emotionally favorable atmosphere;
- formation of motivation to study;
- Cultivating students' knowledge on health issues.
Health-saving technology in the educational process involves organizing training through:
- different channels of information perception (vision, hearing, sensation) depending on the age characteristics of students, as well as the goals and objectives of the lesson;
- creating a health-saving classroom space;
- knowledge of weekly performance zones and planning lessons of varying degrees of difficulty;
- knowledge about the levels of performance of students during the working day;
- planning tests, lessons of new material, generalization lessons, depending on the place of the lesson in the schedule grid;
- distribution of intensity of mental load during the lesson and working day.
Health-saving technologies use the following methods:
- frontal;
- group;
- practical;
- educational game;
- situational method;
- game method;
- competitive;
- active learning methods.
The following techniques are used in health-saving technologies:
- protective and preventive;
- compensatory-neutralizing;
- stimulating;
- informational and educational.
The effectiveness of the analysis of health-saving activities in school depends on methodological and methodological approaches and is built on the principles developed over the previous decades at the Institute of Developmental Physiology of the Russian Academy of Education, namely:
- complexity;
- consistency;
- integrity;
- dynamism (repetition);
- representativeness;
- methodological unity.
Comprehensiveness implies the simultaneous coverage of a wide range of indicators that reflect both the state of the educational environment and personal data characterizing the level and nature of academic and extracurricular workload, as well as the individual adaptive capabilities of the student. Systematicity means the analysis of not only the qualitative and quantitative indicators of the activities of an educational institution, but also (and primarily) the relationships between them, reflecting the structure and effectiveness of the health-preserving activities of an educational institution.
Integrity is a necessary condition for a complete data analysis, implying a comprehensive presentation of the results for each educational institution.
Dynamism (repetition) implies repeated (twice a year - autumn and spring; over a number of years) examination of the same educational institutions, student populations, specific students.
Representativeness (representation) is determined by the requirements of statistics, according to which the reliability of findings and conclusions depends on the size of the sample studied. Representativeness is achieved by surveying sufficiently large populations of students.
Methodological unity is an indispensable condition for the comparability of data obtained at different stages of the study, in different regions, in different educational institutions.
Among the health-saving technologies used in the education system, several groups can be distinguished, which use different approaches to health protection, and, accordingly, different methods and forms of work:
— medical and hygienic technologies (MHT); — physical education and health technologies (PHT); — environmental health-saving technologies (ECT); — technologies for ensuring life safety (LHS); — health-saving educational technologies (HET);
There are other grounds for classifying health-saving technologies. Based on the nature of their action, they can be divided into the following groups:
— protective and preventive; - compensatory-neutralizing; - stimulating; — informational and educational.
The most generalized possible classification is the identification of two types of health-saving technologies - organizational and pedagogical.
The system-forming principle of health-saving pedagogy is the priority of caring for the health of students, within which we can highlight such mandatory conditions as scientific and methodological support for work, selection and training of teaching staff (including care for their health) and, finally, sufficient financial support for the entire project .
Health-saving educational technologies can be divided into three subgroups:
— organizational and pedagogical technologies (OPT), which determine the structure of the educational process, partially regulated in SanPiN, helping to prevent states of overfatigue and physical inactivity;
— psychological and pedagogical technologies (PPT), associated with the direct work of the teacher in the lesson, the impact that he has on his students for all 45 minutes; This also includes psychological and pedagogical support for all elements of the educational process;
— educational and educational technologies (ET), which include programs for teaching competent care of one’s health and creating a culture of health for students, motivating them to lead a healthy lifestyle, preventing bad habits, also providing for organizational and educational work with schoolchildren after school, education their parents.
Health-saving technologies in the work of an individual teacher can be represented as a systemically organized combination of the principles of cooperation pedagogy, “effective” pedagogical techniques, elements of pedagogical skill aimed at achieving optimal psychological adaptation of the student to the educational process, caring for the preservation of his health and education him as a personal example of a culture of health.
A teacher who is ready to use health-saving educational technologies in his work, at the first stage in this regard, faces the following tasks:
— an objective assessment of one’s strengths and weaknesses related to professional activity, drawing up a plan for the necessary self-correction and its implementation;
— necessary advanced training on health issues, health-saving technologies;
— revision of the pedagogical methods and techniques used in their work in terms of their expected impact on the health of students;
— purposeful implementation of health-saving educational technologies during training sessions and extracurricular work with students, monitoring the results obtained, both according to one’s own feelings and using objective assessment methods;
— to promote the formation of a health-preserving educational environment in your educational institution as an effective interaction between all members of the teaching staff, students and their parents to create conditions and implement programs aimed at preserving, developing and strengthening health.
Thus, the main task of implementing health-saving technologies is to organize the educational process at all levels, in which high-quality training, development and education of students are not accompanied by damage to their health.
Observations show that the use of health-saving technologies in the educational process allows students to more successfully adapt to the educational and social space, to reveal their creative abilities, and for the teacher to effectively prevent antisocial behavior.
Bibliography
- Amonashvili, Sh. A. Personal and humane basis of the pedagogical process [Text] / Sh. A. Amonashvili. - M.: Education, 1990.
- Antropova, M.V. Basics of student hygiene [Text] / M.V. Antropova. - M.: Education, 1971.
- Borisova, I. P. Providing health-saving technologies at school [Text] / I. P. Borisova. // Directory of the head of an educational institution. 2005. No. 10. P. 84-92.
- Selevko, G. K. Modern educational technologies [Text] / G. K. Selevko. - M.: Education, 1998.
- Smirnov, N. K. Health-saving educational technologies in modern school [Text] / N. K. Smirnov. - M.: APKiPRO, 2002.
- Sokratova, N.V. Modern technologies for preserving and strengthening the health of children: Textbook [Text] / Ed. ed. N.V. Sokratova. - M.: TC Sfera, 2005.
- Tsabybin, S. A Health-saving technologies in the educational process [Text] /author-comp. S. A. Tsabybin. — Volgograd: Teacher. 2009.
Author: Maria Khudyakova
Health-saving technologies: concept, purpose and objectives. article
Health-saving technologies: concept, purpose and objectives.
Before we start talking about health-saving technologies, let’s define the concept of “technology”. Technology is a tool for the professional activity of a teacher, which is accordingly characterized by a qualitative adjective – pedagogical. The essence of pedagogical technology is that it has a pronounced phasing (step-by-step), includes a set of certain professional actions at each stage, allowing the teacher to foresee the intermediate and final results of his own professional and pedagogical activities during the design process. Pedagogical technology is distinguished by: specificity and clarity of goals and objectives, the presence of stages: primary diagnosis; selection of content, forms, methods and techniques for its implementation; using a set of tools in a certain logic with the organization of intermediate diagnostics to achieve the designated goal; final diagnostics of goal achievement, criteria-based assessment of results. (This definition is proposed by Derkunskaya V.A. - Candidate of Pedagogical Sciences) What are health-saving technologies? Health-saving technologies in preschool education are technologies aimed at solving the priority task of modern preschool education - the task of preserving, maintaining and enriching the health of the subjects of the pedagogical process in kindergarten: children, teachers and parents. The goal of health-saving technologies in preschool education in relation to a child is to ensure a high level of real health for a kindergarten pupil and the education of valeological culture as the totality of a child’s conscious attitude to health and human life, knowledge about health and the ability to protect, support and preserve it, valeological competence, allowing a preschooler independently and effectively solve problems of a healthy lifestyle and safe behavior, tasks related to the provision of basic medical, psychological self-help and assistance.
The objectives of health-saving technologies are;
1. Preservation and strengthening of children’s health based on the integrated and systematic use of physical education means available to kindergartens and optimization of physical activity in the fresh air.
2. Ensuring an active position for children in the process of gaining knowledge about a healthy lifestyle.
3. Constructive partnership between the family, the teaching staff and the children themselves in strengthening their health and developing their creative potential.
Types of health-saving technologies used in preschool educational institutions
Types of health-saving technologies in preschool education - classification of health-saving technologies according to the dominance of goals and tasks to be solved, as well as the leading means of health-saving and health-enrichment of subjects of the pedagogical process in kindergarten. Health-saving activities in kindergarten are carried out in the following forms: Medical and preventive technologies. Medical and preventive activities ensure the preservation and enhancement of children’s health under the guidance of preschool medical personnel in accordance with medical requirements and standards using medical supplies. The objectives of this activity are: - organization of monitoring of children's health and development of recommendations for optimizing children's health; - organization and control of children's nutrition, physical development, hardening; - organization of preventive measures that contribute to the resistance of the child's body (for example, immunization, gentle treatment during the adaptation period, etc. .d.) - organization of control and assistance in ensuring the requirements of sanitary and epidemiological standards - San PiNov - organization of a health-preserving environment in preschool educational institutions. Monitoring of the health status and physical development of children is carried out by kindergarten medical workers. All work on the physical education of children in preschool educational institutions is based on their physical fitness and existing deviations in health. To do this, based on individual medical records, the preschool doctor draws up a summary diagram for each age group, which helps educators and medical workers have a clear picture of the health status of the children of the entire group and each child individually. This analysis scheme and specific recommendations are entered into the group “Health Log” - “Child’s Individual Route” - so that each teacher plans physical education and health activities in accordance with the children’s health characteristics.
Physical education and health technology. Physical education and health activities are aimed at the physical development and strengthening of the child’s health. The objectives of this activity are: - development of physical qualities; — control of motor activity and the development of physical education in preschool children, — formation of correct posture, prevention of disorders of the musculoskeletal system; - fostering the habit of daily physical activity; - health improvement by means of hardening. Physical education and health activities are carried out by a physical education instructor during physical education classes, as well as by teachers - in the form of various gymnastics, physical education sessions, dynamic breaks, etc.;
Technologies for ensuring the socio-psychological well-being of the child. The purpose of this activity is to ensure emotional comfort and positive psychological well-being of the child in the process of communicating with peers and adults in kindergarten and family; ensuring the social and emotional well-being of a preschooler, because emotional mood, mental well-being, cheerful mood of children is important for their health. In its activities, the “escort service” is guided by the regulations on the medical-psychological-pedagogical service and aims to create an integral system in a preschool institution that provides optimal conditions for the development of children, taking into account age and individual characteristics, the state of somatic and mental health. In this system, diagnostic, advisory, correctional and developmental, treatment and preventive and social areas interact.
Technologies for health preservation and health enrichment of teachers. Improving the health of children and their favorable physical development is influenced by the entire way of life of a child in kindergarten, the caring and attentive attitude of adults towards him, and the high sense of responsibility of the entire team for each pupil. Therefore, much attention in preschool educational institutions is paid to the selection and placement of personnel into groups, taking into account their business qualities, experience and psychological compatibility. Bearing in mind that the results of physical development depend primarily on the professional training of teachers and their pedagogical knowledge, a system of comprehensive methodological work to improve skills has been thought out. A teacher who guards the health of the child, who fosters a culture of health for the child and parents, must first of all be healthy himself, have valeological knowledge, not overworked, must be able to objectively assess his strengths and weaknesses associated with professional activities, draw up a plan for the necessary self-correction and begin its implementation.
Technologies of valeological education of parents. The main educators of the child are the parents. The child’s mood and state of physical comfort depend on how the child’s daily routine is properly organized and how much attention parents pay to the child’s health. The healthy lifestyle of a child, to which he is taught in an educational institution, can either find daily support at home, and then be consolidated, or not be found, and then the information received will be unnecessary and painful for the child. Information and educational activities are expressed in the formation of a healthy lifestyle as a value among parents, as well as in introducing parents to various forms of physical education in a preschool institution, informing about the state of health and physical development, and the level of motor readiness of their child; involving parents in participating in various joint physical education activities and holidays. In order to cooperate with parents in promoting a healthy lifestyle in children, we have developed a system of events, which include: parent meetings, consultations, competitions, sports events, health events, family clubs, moving folders, conversations, personal example of a teacher, non-traditional forms of working with parents, practical demonstrations (workshops).
Health-saving educational technologies. This type of activity involves the education of a valeological culture, or a culture of health, in preschool children. Its goal is to form in children a conscious attitude towards health and life, accumulation of knowledge about health and development of skills to protect it. Health-saving educational technologies are the most significant among all known technologies in terms of the degree of influence on children’s health. Their main feature is the use of psychological and pedagogical techniques, methods, and approaches to solving emerging problems. Educational activities involve conducting classes and conversations with preschoolers about the need to maintain a daily routine, the importance of hygienic and physical culture, about health and means of strengthening it, about the functioning of the body and the rules of caring for it, children acquire cultural and healthy lifestyle skills, knowledge of the rules of safe behavior and reasonable actions in unforeseen situations.
Preparing a child for a healthy lifestyle based on health-saving technologies should become a priority in the activities of every educational institution for preschool children.