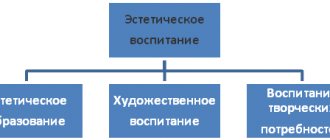
Purpose of music education in preschool educational institutions
Definition 1
Musical education is a specially organized process of influence through the means of musical art, through which the aesthetic development of a child is realized, the foundations of his general culture are formed, and value guidelines are developed.
Musical education has a positive impact on personal development.
Music influences the formation of the creative component of the individual and contributes to the development of the creative foundations of his activity. and this, in turn, leads to the harmonious development of the child and the formation of all his qualities necessary for successful social life.
The main purpose of music education is the comprehensive harmonious development of the child’s personality. A number of subgoals of music education can be distinguished:
Are you an expert in this subject area? We invite you to become the author of the Directory Working Conditions
- Introducing a preschooler to the art of music. The child learns the basics of musical creativity, learns the aesthetic perception of music, and develops musical taste.
- Mastering the fundamentals of musical culture. Through it, the child learns the basics of general culture and forms his own views, attitude towards art, and develops his own line of cultural behavior.
- Development of musical abilities of a preschooler. Through musical education, a sense of rhythm, musical memory, auditory attention and perception are formed, which ultimately contributes to the formation of musical taste.
- Formation of the need for music. The need for musical creativity leads to the creative development of a preschooler.
- Implementation of different types of musical and artistic creativity of preschool children. In this way, the child can assert himself and realize himself in a creative direction, satisfy his creative needs.
Music classes in preschool educational institutions are aimed at developing in preschoolers a love of music, an interest in art, and the development of adequate musical taste and orientation skills in musical information.
Finished works on a similar topic
Course work Musical education of preschool children in preschool educational institutions 400 ₽ Abstract Musical education of preschool children in preschool educational institutions 220 ₽ Test work Musical education of preschool children in preschool educational institutions 240 ₽
Receive completed work or specialist advice on your educational project Find out the cost
CHILDHOOD GUIDE
Musical development is the result of a child’s formation in the process of active musical activity. The process of a child’s musical development is the interaction and interdependence of fundamental factors: - the child’s own nature (inner world); — external environment (external world); - musical activity of the child.
Musical education of preschool children includes: - a set of formed emotional, intellectual, personal and behavioral qualities of the child; - achievement of a certain level of musical culture.
The musical culture of a preschooler includes: - emotional responsiveness to highly artistic works of musical art; - musical-imaginative thinking and imagination; — experience in creative musical activity; - musical and aesthetic consciousness.
Music education is music education and music training . Musical education is an organized pedagogical process aimed at developing an emotional and value-based attitude towards the world, people around and oneself based on the appropriation of the moral and aesthetic content of music. Musical learning is the process of transferring and mastering knowledge, skills and methods of action necessary for the successful implementation of musical activity.
Means of musical expression 1. Intonation, conveying the emotional state, mood of a musical work. 2. Timbre – color of sound. 3. Rhythm - a sequence of sounds of the same and different durations. 4. Tempo – speed of music performance. 5. Mode – an ordered relationship of sounds in height (major and minor). 6. Dynamics - the strength of the sound of music. 7. Register – a series of sounds that are similar in timbre coloring. 8. Melody is a musical idea expressed through sounds in modal and meter-rhythmic relationships. 9. Harmony - combining sounds into consonances.
The content of music education for preschool children: 1) the experience of the child’s emotional and moral attitude to the surrounding reality, embodied in music; 2) musical knowledge, skills and abilities; 3) experience in musical and creative activities.
Forms of organizing musical activities in preschool educational institutions: Classes are the main form of organization in which children are taught, their abilities are developed, personality traits are nurtured, and the foundations of musical and general culture are formed. The main task is to arouse children’s interest in music and musical activities. The development of children’s emotional responsiveness to music throughout the lesson should be the focus of the teacher’s attention.
The content of music classes in preschool educational institutions: Typical includes all types of musical activities. The dominant one is dominated by some type of musical activity (dance-rhythmic activity, song performance). At the thematic stage , one topic is selected that unites all types of musical activities. Complex contains various types of art, types of artistic activity (integrated).
Music in the everyday life of preschool educational institutions: - use of music in everyday life (listening to records, independent music playing, exercises, games, morning exercises); - various types of entertainment (themed musical evenings, talks and concerts, theatrical performances, attractions), - holiday matinees.
Methods of music education for preschool children These are methods of interrelated activities between the teacher and children, aimed at developing musical abilities and forming the foundations of the musical culture of preschool children. The main methods are visual, verbal and practical . Each of the three methods should be used with increasing difficulty: from direct influence (explanatory and illustrative method) through reinforcement, exercise, creating search situations (showing options for completing a task) to problem-based education and training (children’s independent search for ways to act). Creating problem situations in the classroom helps develop the independence of preschoolers and the creative use of developed skills and abilities. Visual method (visual-auditory and visual-visual) Visual-auditory is the leading method of musical education - the performance of musical works by a teacher or the use of TSO. Options for the problematic use of the visual-auditory method (creating a problem situation): - compare “live” sound and recording; - compare 2-3 works that contrast with each other. The visual method has an auxiliary value (paintings, drawings, cards). Examples of problematic use of this method: - choose one of three paintings that matches the nature of the music; - compare 2-3 pieces of music with the picture and choose the one closest to it in figurative content.
Verbal method - conversation, story, explanation, clarification, etc. The peculiarity of the method in music education: it requires not everyday, but figurative speech. In this case, the teacher must have bright, competent, expressive, emotional speech. The method most often is not problematic, but it can be problematic if children are encouraged to make comparisons and make independent statements (about character, genre, means of expression).
A practical method is to demonstrate performing techniques in singing, movements, and playing instruments. The method becomes problematic when the teacher shows more than one option for performing actions: - it is proposed to choose from several movements the one that is more suitable for the nature of the music; - you are invited to find one or more options for movements yourself in accordance with the music.
The choice of methods depends on the age of the children: in early preschool age, the proportion of visual and practical methods is large. Children do not yet have access to the widespread use of verbal methods. Their speech is not yet developed. Therefore, the teacher uses techniques that encourage children to use new words and at the same time make this task easier. When working with older children, all methods and techniques are used with a greater degree of challenge, which stimulates the expression of independence and creativity.
All of these methods contribute to music education (i.e. training and education) and musical development of preschool children. The choice of methods also determines the stage of work on a piece of music: Stage 1 - the leading place is occupied by visual-auditory and verbal methods. Stage 2 - the role of the practical method increases, demonstrating performance techniques (including variable ones) in combination with visual and verbal ones. Stage 3 - (the work has been learned) the practical method acquires a large share of variability, independence and creativity.
Dear teachers! If you have questions about the topic of the article or have difficulties in working in this area, then write in the comments . I'll definitely help.
Golovina Bela Gennadievna, site administrator.
Methodology for conducting the “Musical Living Room” in a preschool educational institution Development of the emotional responsiveness of preschool children through the perception of music Musical development of young children Federal State Educational Standard of Preschool Education: musical development >
Forms of organizing music education in preschool educational institutions
Musical education in preschool educational institutions is implemented in the following forms:
- Musical lessons. They are educational musical activities. During music lessons, the child’s intellectual, moral, aesthetic and cultural development is carried out. Musical classes include different types and areas of musical activity: singing, playing instruments, dancing, listening to music of different genres, getting acquainted with the work of great composers, mastering musical literacy.
- Independent musical activity of preschool children. It is associated with children demonstrating their creative abilities. They need to be encouraged to do this. Children apply their musical knowledge and focus it on their interests and needs.
- Music in everyday life. Music is becoming an important component of all types of preschool activities. It permeates all routine moments of the day. For example, music turns on when children are charging, it accompanies the gameplay. Getting ready for a walk can be accompanied by singing, etc. In addition, the preschool educational institution organizes holidays that are accompanied by musical performances.
- Musical education in the family. It is important to establish interactions with parents and form a unified direction of musical education. If music accompanies all the routine moments of a preschooler in a preschool educational institution, then at home it should also accompany the child. For example, a mother can find out what music the teacher plays during exercise and use it. At night you can sing a lullaby, etc. It is important that music be a constant component of a child’s life. An episodic nature will not give the desired educational effect.
The purpose and objective of educational activities
The goal and task of educational activities is to instill in preschoolers an interest in art, the ability to understand musical information , genres, musical forms , and to contribute to the formation of artistic taste in children.
Educational activity is the main form of educational activity in kindergarten and the educational process is carried out through direct instruction. In everyday life, the indirect guidance of the music director , teacher , and parents in the musical education of children .
Direct teaching in everyday life is not completely excluded, but it should be limited. Any musical communication with a child should be built on joint activity, partnership, encouraging his initiative in every possible way, which is especially important when children exhibit independent musical expressions . Music in the everyday life of a kindergarten combines all forms of musical activity : holidays, entertainment, morning exercises.
So, the form of organizing music education in the everyday life of a kindergarten provides for two types of guidance from the teacher , music director , and parents: direct and indirect. During games, educational exercises, and walks, music can be played at the request of both children and adults.
But in entertainment, holidays, morning exercises, this happens, as a rule, on the initiative of the teacher; at the same time, he must, of course, take into account the capabilities, interests and passions of the children. The interaction of the entire teaching staff is one of the signs of a highly effective organization of the educational process.
The music director creates conditions for children to acquire knowledge, skills and abilities in various types of musical activities , and the teacher helps to consolidate them.
In order for music to become firmly established in children’s lives, the music director needs to build interaction not only with the team of teachers, but also with parents. To do this, certain work is carried out with parents, during which it is necessary to ensure that they become conductors of the child’s cultural formation. Children and adults love general forms of interaction , and these are holidays, entertainment, competitions, quizzes.
Club work also contributes to the emergence of independent musical activity in children, both in a group and at home with their parents. the accumulated musical experience into everyday life in accordance with his interests and desires.
The emergence of independent musical activity in kindergarten is one of the indicators of a high level of development of children, characterized by certain musical skills and abilities , the ability to transfer a variety of musical activities into everyday life.
The child must be able to apply the accumulated musical experience , developed musical skills and abilities in new conditions, in independent musical activities according to his interests and desires.
The structure of a music lesson in a preschool educational institution
Music classes at preschool educational institutions consist of the following components:
- Introductory part. It is aimed at preparing preschoolers to become familiar with music. In the introductory part of the lesson, you can include physical education components: performing movements to music, performing dance steps. This stimulates the preschooler’s musical activity and makes music lessons more productive.
- Listening to music. This part is focused on developing preschoolers’ skills in aesthetic perception of musical creativity and the formation of musical perception.
- Singing and song creativity. Children sing songs of different genres and also learn to compose songs on their own. Independent composing of a song motivates a preschooler’s interest in the art of music and helps to reveal his creative potential.
- Learning to play musical instruments. Typically, instruments are selected that are accessible to a specific age group. The teacher demonstrates their sound and shows the basics of playing melodies. Then the children themselves try to master playing this or that instrument.
- Dance activity. Dancing promotes the development of musical rhythm and creates a positive attitude towards music, because dancing is fun.
- Game activity. It is not a component of every music lesson, but may be included periodically. The game helps to absorb musical information more productively.
Types of musical activities
The standard defines age-appropriate activities, including musical activities for children.
In infancy (2 months - 1 year) - this is direct emotional communication with an adult, manipulation with objects and cognitive research activities, perception of music, children's songs and poems, motor activity and tactile-motor games.
At an early age (1 year - 3 years) - these are object-based activities and games with composite and dynamic toys, experimenting with materials and substances (sand, water, dough, etc.), communication with an adult and joint games with peers under the guidance of an adult, self-service and actions with household tools (spoon, scoop, spatula, etc.), perception of the meaning of music, fairy tales, poems, looking at pictures, motor activity.
For preschool children (3 years - 8 years) - this is a gaming activity, including role-playing games as the leading activity of preschool children, as well as games with rules and other types of games, communicative (communication and interaction with adults and peers), cognitive - research (studying objects of the surrounding world and experimenting with them), perception of fiction and folklore, self-service and basic household work (indoors and outdoors), construction from various materials, including construction sets, modules, paper, natural and other materials, visual arts (drawing, modeling, appliqué), musical (perception and understanding of the meaning of musical works, singing, musically rhythmic movements, playing children's musical instruments) and motor (mastery of basic movements) forms of activity of the child.
Based on the age-appropriate types of activities proposed by the Standard, it becomes possible to specify the forms of musical activity with children of early and preschool age (table). Please note that the proposed forms of a practice-oriented nature primarily grow out of the child’s cultural practices.
Conditions for the effective organization of music education in preschool educational institutions
In order for musical education to be productive, a number of conditions for its organization must be observed:
- Taking into account the age and individual characteristics of preschool children when planning a music lesson;
- Focus on the musical development of preschool children not only during music lessons, but in everyday life;
- The content of music classes should reflect the purpose of music education;
- The results of a preschooler’s musical development should be noticeable in the child’s daily activities - he transfers his knowledge and skills into his life activities;
- The teacher does not have an active educational influence on the musical development of the preschooler. The teacher identifies himself as an equal partner in joint musical activities, giving the child maximum independence in musical knowledge and development.
Get paid for your student work
Coursework, abstracts or other works